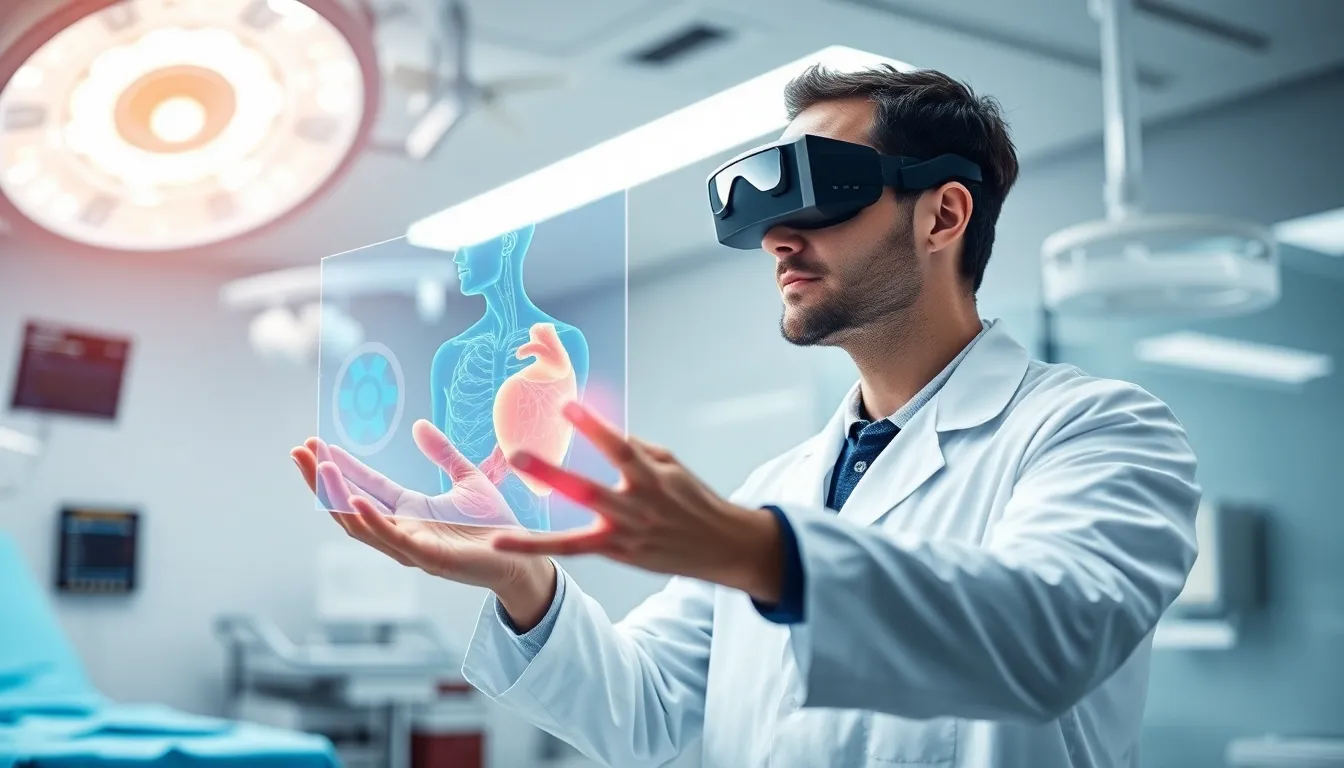
Imagine a world where doctors don’t just rely on their trusty stethoscopes but also don a pair of sleek augmented reality glasses. Sounds like something out of a sci-fi movie, right? Well, welcome to the future of healthcare, where augmented reality (AR) is transforming patient care and medical training faster than you can say “virtual scalpel.”
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of Augmented Reality in Healthcare
Augmented reality (AR) enhances the healthcare field by overlaying digital information onto the physical world. Through the use of AR technologies, medical professionals access real-time data during procedures, improving accuracy and efficiency. Surgical simulations, guided by AR, assist in training new surgeons by creating realistic environments for practice.
In medical education, AR provides students with interactive learning experiences. Digital anatomy models enable learners to explore the human body in detail, fostering a deeper understanding of complex systems. Additionally, AR applications allow remote experts to guide on-site personnel through complex tasks, reducing errors and improving outcomes.
Patient care benefits from AR as well. For instance, visualizing treatment plans helps patients understand their conditions and procedures better. Doctors can demonstrate upcoming surgeries using AR, increasing patient comfort and trust in medical decisions.
Furthermore, AR impacts rehabilitation by creating engaging exercises for patients recovering from injuries. Tailored programs can utilize AR to motivate individuals, making recovery more interactive.
A study highlighted that 60% of healthcare professionals believe AR improves surgical precision. Another report suggests that AR in education raises retention rates by up to 30%. These statistics underscore the potential of AR to revolutionize both training and patient engagement in healthcare.
Embracing these advancements facilitates better communication among healthcare providers and their patients. Rapid developments in AR technologies promise ongoing improvements in treatment, education, and training, ultimately enhancing the quality of healthcare services.
Applications of Augmented Reality
Augmented reality transforms key areas in healthcare by enhancing visualization and interactivity. Its applications extend notably to surgical guidance, medical training, and patient care.
Surgical Guidance
Surgical guidance utilizes augmented reality to overlay crucial information during operations. Surgeons access real-time imaging and data, directing their focus precisely. For instance, AR systems provide 3D visualizations of patient anatomy, improving situational awareness in complex procedures. Enhanced accuracy leads to reduced complications, translating into better patient outcomes. Incorporating AR into surgery has shown a significant increase in surgical precision, with 60% of healthcare professionals affirming its effectiveness.
Medical Training and Education
Medical training benefits greatly from augmented reality’s interactive features. Students interact with lifelike 3D anatomy models, enriching their understanding of complex structures. Traditional learning methods often lack engagement; however, AR creates dynamic environments for practical experiences. Training through realistic simulations fosters muscle memory, essential for developing surgical skills. Research indicates AR can boost information retention rates by up to 30%, highlighting its value in education.
Patient Care and Rehabilitation
Augmented reality enhances patient care by improving communications around treatment plans. Visual aids assist patients in comprehending conditions and procedures, fostering trust in their healthcare providers. For rehabilitation, AR facilitates engaging exercise routines tailored to individual needs, motivating patients through enjoyable experiences. These technology-driven approaches not only streamline recovery processes but also elevate overall patient satisfaction. Providing visual context strengthens the connection between patients and medical staff, ultimately improving adherence to treatment.
Benefits of Augmented Reality in Healthcare
Augmented reality (AR) offers substantial benefits in healthcare, enhancing both clinical practice and patient experiences.
Enhanced Visualization
AR provides unique visualization capabilities in medical environments. Doctors and surgeons can overlay digital models onto a patient’s anatomy during procedures. This 3D representation facilitates a clear understanding of complex structures. Surgeons gain improved situational awareness, which ultimately minimizes the risk of errors. Statistics reveal that 60% of healthcare professionals perceive AR as a tool that increases surgical precision. Medical professionals can visualize crucial data in real-time, allowing for immediate adjustments and informed decisions. Practical applications of AR not only aid in surgical settings but also assist in diagnostic imaging, making interpretation more straightforward for clinicians.
Improved Patient Outcomes
AR significantly contributes to improved patient outcomes. By visualizing treatment plans, patients can better grasp their medical conditions and the steps required for recovery. This understanding fosters greater trust in healthcare providers, enhancing communication between patients and clinicians. AR also plays a vital role in rehabilitation by offering tailored exercise routines that engage patients and motivate them to participate actively in their recovery process. Personalized experiences, driven by augmented reality, lead to higher rates of patient satisfaction. Engaging patients in their treatment reflects positively on overall healthcare quality, promoting a more holistic approach to wellness and recovery.
Challenges and Limitations
Augmented reality in healthcare faces several challenges and limitations that impact its integration into standard practices.
Technical Barriers
Technical barriers pose significant challenges for healthcare providers adopting augmented reality. High costs associated with AR hardware like smart glasses can limit accessibility. Additionally, compatibility issues with existing medical equipment hinder seamless integration. Relying on robust software requires extensive testing to ensure reliability during procedures. Also, data privacy concerns arise since AR systems collect sensitive patient information. Vendors must ensure compliance with regulations such as HIPAA, which adds complexity to deployment.
Acceptance and Adoption
Acceptance and adoption of augmented reality technology present hurdles within healthcare organizations. Some medical professionals are hesitant to embrace new technology due to a lack of training or familiarity. Resistance to change often stems from discomfort with altering established processes. Integration into daily workflows requires overcoming these perceptions and ensuring usability. Stakeholders must communicate the benefits, like improved surgical precision and enhanced patient engagement, to foster a more productive environment. Statistically, building awareness among staff can enhance participation and drive adoption rates, which are crucial for successful integration.
Future Trends in Augmented Reality
Augmented reality continues to advance, promising new developments in healthcare practices. Innovations in technology significantly enhance its application in medical fields.
Innovations in Technology
Cutting-edge AR devices are arriving on the market, featuring improved graphics and functionality. New software applications enable precise tracking of patient anatomy, which supports complex procedures. Developers are creating more user-friendly interfaces that require less training, making them accessible for various healthcare professionals. Enhanced integration of AR with artificial intelligence provides personalized treatment options based on real-time data analysis. Research shows that by improving visualization and interaction, AR can increase knowledge retention among medical staff. Hospitals and clinics are beginning to adopt these innovative tools, fostering a more interactive environment that prepares professionals for the challenges they will face.
Potential for Expanded Uses
Expanding the uses of AR in medicine holds incredible promise for future applications. Remote consultations become more effective when doctors can visualize a patient’s condition through AR tools. Emergency response teams utilize AR in rapid assessments, improving decision-making during critical situations. Patient education programs benefit from interactive AR visuals, which enhance understanding of medical procedures. Rehabilitation specialists promote adherence to therapy plans through engaging AR exercises. This technology’s versatility supports numerous healthcare areas, paving the way for advanced treatment methods and improved patient outcomes. As the technology matures, its applications are expected to broaden, transforming the healthcare landscape.
Augmented reality is poised to redefine the healthcare landscape by enhancing both patient care and medical training. As AR technology continues to evolve it promises to bridge gaps in communication and understanding between healthcare providers and patients. The potential for improved surgical precision and interactive learning experiences underscores its transformative power.
While challenges like costs and data privacy remain obstacles the ongoing advancements in AR technology indicate a bright future. With increased accessibility and integration with artificial intelligence the benefits of AR in healthcare will likely expand further. Embracing this innovation could lead to more effective treatments and a more engaged patient population ultimately shaping a new era in healthcare.





